使用 NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo 控制語言模型生成
使用語言模型生成文字通常涉及根據機率分佈選擇下一個 token。貪婪搜尋之類的直接方法會選擇最有可能的 token,但這可能導致通用或重複的輸出。為了增加多樣性和控制,更高階的解碼策略,如束搜尋、核取樣和 top-k 取樣,被廣泛使用。這些策略由 🤗 Transformers 庫支援,使我們能夠靈活地塑造模型的輸出。
但是,如果我們想更進一步,透過直接修改機率分佈來控制文字生成過程本身,那該怎麼辦呢?這就是logit 處理發揮作用的地方。Hugging Face 的 LogitsProcessor API 允許您自定義語言模型頭的預測分數,從而對模型行為進行細粒度控制。🤗 Transformers 庫不僅提供了一組豐富的內建 logits 處理器,還使社群能夠建立和共享針對獨特用例的自定義處理器。
NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo 應運而生,它是一系列功能強大、模組化的 logits 處理器,旨在完成特定任務,例如控制序列長度、強制使用關鍵短語或指導多項選擇答案。NVIDIA 的庫與 Hugging Face 的 generate 方法完全相容,是 logits 處理領域社群驅動創新的一個絕佳範例。
在這篇文章中,我們將探討 NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo 如何增強和擴充套件現有功能,深入探討其特性並演示它如何最佳化您的 AI 工作流程。
語言模型中的 Logits 是什麼?
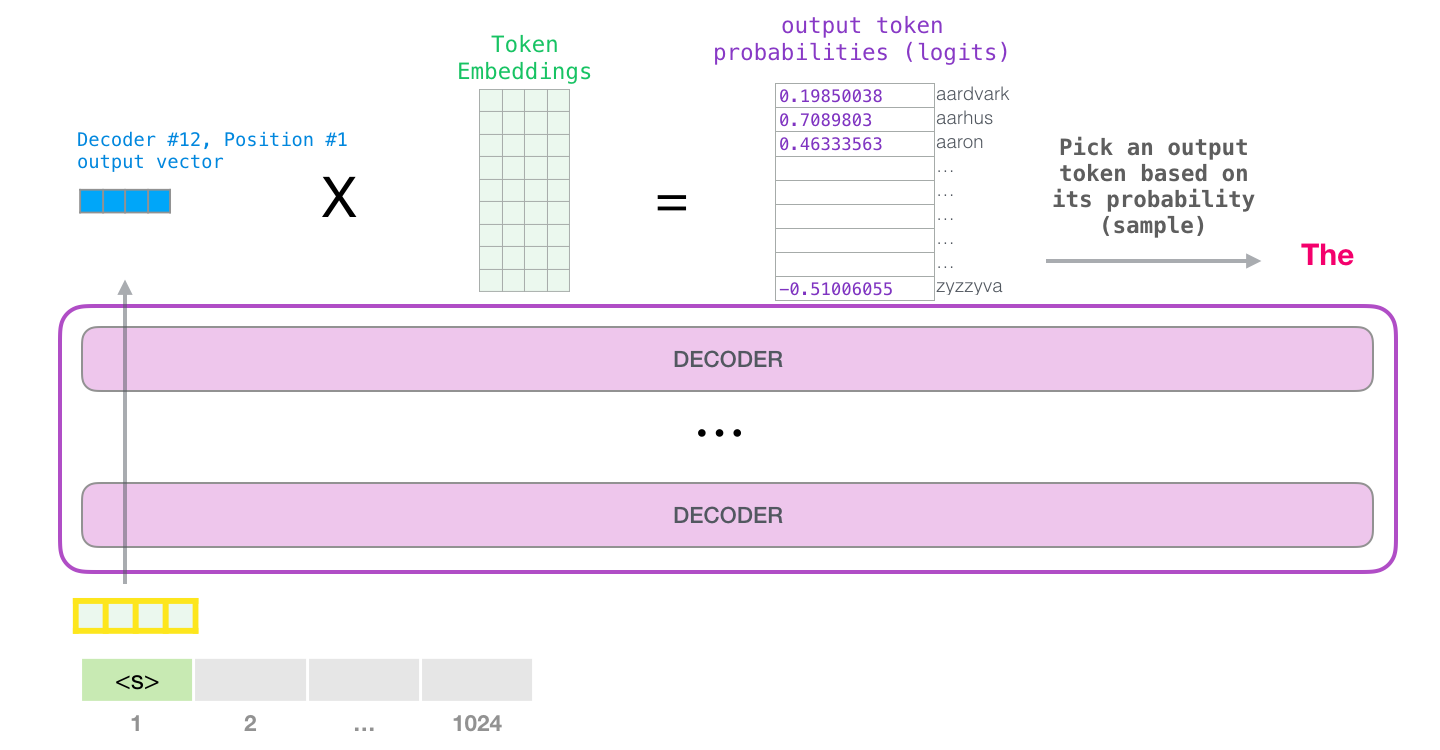 摘自:https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-gpt2/
摘自:https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-gpt2/
Logits 是語言模型為其詞彙表中的每個 token 生成的原始、未歸一化的分數。這些分數透過 softmax 函式轉換為機率,從而指導模型選擇下一個 token。
以下是 logits 如何適應生成過程的示例:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
# Load a model and tokenizer
model_name = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
# Input text
prompt = "The capital of France is"
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# Get logits
with torch.inference_mode():
outputs = model(**inputs)
logits = outputs.logits
# Logits for the last token
last_token_logits = logits[:, -1, :]
這些 logits 代表模型對每個潛在的下一個詞的置信度。使用 softmax,我們可以將它們轉換為機率並解碼為生成的文字。
# Prediction for the next token
next_token_probs = torch.nn.functional.softmax(last_token_logits, dim=-1)
# Decode logits to generate text
predicted_token_ids = torch.argmax(next_token_probs, dim=-1)
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(predicted_token_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
print("Generated Text:", generated_text[0])
>>> Generated Text: Paris
雖然此管道演示了原始 logits 如何轉換為文字,但值得注意的是 🤗 Transformers 簡化了此過程。例如,generate() 方法會自動處理這些轉換,包括應用 softmax 函式和從機率分佈中取樣。
然而,原始 logits 對於取樣或施加任務特定約束等常見任務可能不理想。有關在生成過程中有效處理 logits 的更多詳細資訊,請參閱 Hugging Face 的生成部落格文章。這就是logit 處理變得不可或缺的原因,它可以根據特定需求調整輸出。
為什麼要處理 Logits?
在控制輸出行為時,原始 logits 常常力不從心。例如:
- 缺乏約束:它們可能不遵守所需的格式、語法規則或預定義的結構。
- 過度概括:模型可能優先選擇通用響應,而不是特定、高質量的輸出。
- 任務不匹配:序列可能過早結束、過於冗長或遺漏關鍵細節。
Logit 處理使我們能夠在生成之前透過修改這些原始分數來調整模型的行為。
NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo
NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo 透過針對特定任務量身定製的模組化元件簡化了 logits 的後處理。讓我們探索其功能並瞭解如何使用它們。要跟隨操作,請前往此筆記本並嘗試 logits 處理器。
使用以下命令安裝庫:
pip install logits-processor-zoo
為了演示處理器,我們將建立一個簡單的 LLMRunner 類,該類初始化模型和分詞器,並公開 generate_response 方法。然後我們將向 generate_response 方法提供不同的處理器,並觀察它們的作用。
# Adapted from: https://github.com/NVIDIA/logits-processor-zoo/blob/main/example_notebooks/transformers/utils.py
class LLMRunner:
def __init__(self, model_name="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct"):
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
)
def generate_response(self, prompts, logits_processor_list=None, max_tokens=1000):
if logits_processor_list is None:
logits_processor_list = []
for prompt in prompts:
conversation = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
inputs = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
conversation,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_dict=True,
).to(self.model.device)
outputs = self.model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=max_tokens,
min_new_tokens=1,
logits_processor=LogitsProcessorList(logits_processor_list),
)
gen_output = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(
outputs, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
)
# Extract only the generated output after the original input length
generated_text = gen_output[0][
len(
self.tokenizer.decode(
inputs["input_ids"][0], skip_special_tokens=True
)
) :
].strip()
print(f"Prompt: {prompt}")
print()
print(f"LLM response:\n{generated_text}")
runner = LLMRunner()
1. GenLengthLogitsProcessor
透過調整序列結束 (EOS) token 的可能性來控制生成序列的長度。
此處理器在需要控制生成文字長度的場景中特別有用,例如生成簡潔摘要、限制冗餘輸出或根據特定用例定製響應。例如,它可以幫助確保聊天機器人提供簡短而有意義的響應,同時透過在需要時完成句子來保持語法完整性。
example_prompts =[
"Tell me a story about a kid lost in forest."
]
# generate short response
print(runner.generate_response(
example_prompts,
[GenLengthLogitsProcessor(runner.tokenizer, boost_factor=0.1, p=2, complete_sentences=True)]
))
LLM 響應:從前,在一片茂密的森林裡,住著一個名叫蒂米的小男孩。蒂米和他的父母以及小妹妹艾瑪一起參加了家庭露營旅行。他們已經走了好幾個小時,茂密的樹木似乎把他們圍了起來。當太陽開始下山時,蒂米意識到他已經離家遠去了。起初,蒂米沒有驚慌。他想叫喊他的父母和艾瑪,但他的聲音因為唱篝火歌曲而嘶啞。他環顧四周,但樹木似乎永遠延伸著,使得他無法看到任何熟悉的標誌物。隨著夜幕降臨,蒂米的恐懼開始蔓延。
# generate long response
print(runner.generate_response(
example_prompts,
[GenLengthLogitsProcessor(runner.tokenizer, boost_factor=-10.0, p=0, complete_sentences=False)]
))
LLM 響應:從前,在茂密而充滿活力的森林裡,住著一個名叫馬克斯的小男孩。馬克斯是一個好奇心強、喜歡冒險的八歲孩子,他熱愛探索戶外。一個陽光明媚的下午,當他在森林裡漫步時,他偶然發現了一條他從未見過的小徑。馬克斯對這個發現感到興奮,決定沿著小徑走,看看它會通向哪裡。森林裡生機勃勃,陽光透過樹木過濾下來,營造出一種神奇的氛圍。馬克斯走了大約 20 分鐘,他的眼睛掃視著周圍,尋找任何文明的跡象。當太陽開始下山,給森林投下溫暖的橙色光芒時,馬克斯意識到他迷路了。他沒有電話,沒有錢包,也無法與家人聯絡。恐慌開始蔓延,馬克斯開始感到害怕和孤獨。驚慌失措的馬克斯開始在森林裡奔跑,心跳加速,雙腿顫抖。他偶然發現了一片空地,看到了遠處微弱的光線。當他靠近時,他看到了空地中央的一個小木屋。煙囪裡冒著煙,馬克斯能聽到有人輕輕哼唱的歌聲。...
在上面的示例中,我們使用 `GenLengthLogitsProcessor` 來縮短和延長模型生成的響應。
2. CiteFromPromptLogitsProcessor
提升或降低提示中的 token,以鼓勵類似的輸出。
這在需要上下文保留的任務中尤其有價值,例如根據段落回答問題、生成包含特定細節的摘要或在對話系統中產生一致的輸出。例如,在分析使用者評論的給定程式碼片段中,此處理器確保模型生成與評論內容密切相關的響應,例如強調對產品價格的看法。
example_prompts =[
"""
A user review: very soft, colorful, expensive but deserves its price, stylish.
What is the user's opinion about the product's price?
""",
]
# Cite from the Prompt
print(runner.generate_response(
example_prompts,
[CiteFromPromptLogitsProcessor(runner.tokenizer, example_prompts, boost_factor=5.0)],
max_tokens=50,
))
LLM 響應:根據使用者評論,使用者對產品價格的看法是:使用者非常滿意,但價格昂貴,但產品時尚、柔軟、色彩豐富,這是使用者願意支付的價格。
請注意生成如何引用輸入提示。
3. ForceLastPhraseLogitsProcessor
強制模型在其輸出結束前包含特定短語。
此處理器在結構化內容生成場景中特別有用,在這些場景中,一致性或遵守特定格式至關重要。它非常適合生成引用、正式報告或需要特定措辭以保持專業或有條理的呈現的輸出等任務。
example_prompts = [
"""
Retrieved information from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bulbasaur
Bulbasaur is a fictional Pokémon species in Nintendo and Game Freak's Pokémon franchise.
Designed by Atsuko Nishida, Bulbasaur is a Grass and Poison-type, first appearing in Pocket Monsters: Red and Green (Pokémon Red and Blue outside Japan) as a starter Pokémon.
Since then, it has reappeared in sequels, spin-off games, related merchandise, and animated and printed adaptations of the franchise.
It is a central character in the Pokémon anime, being one of Ash Ketchum's main Pokémon for the first season, with a different one later being obtained by supporting character May.
It is featured in various manga and is owned by protagonist Red in Pokémon Adventures.
What is Bulbasaur?
""",
]
phrase = "\n\nReferences:"
batch_size = len(example_prompts)
print(runner.generate_response(
example_prompts,
[ForceLastPhraseLogitsProcessor(phrase, runner.tokenizer, batch_size)]
))
LLM 響應:根據維基百科文章檢索到的資訊,妙蛙種子是《寶可夢》系列中的虛構寶可夢。它是一種草系和毒系的寶可夢,並出現在各種媒體形式中,包括: - 作為第一代寶可夢遊戲(包括《寶可夢紅》和《寶可夢藍》)中的初始寶可夢。 - 作為寶可夢動畫中的主要角色,它是小智最早的寶可夢之一。 - 作為寶可夢漫畫中的角色,由主角小赤擁有。 - 作為各種其他寶可夢媒體中的角色,例如衍生遊戲和相關商品。妙蛙種子也是寶可夢繫列的核心角色,經常與其他寶可夢一起出現,是寶可夢世界的關鍵組成部分。參考資料:- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bulbasaur
phrase = "\n\nThanks for trying our RAG application! If you have more questions about"
print(runner.generate_response(example_prompts,
[ForceLastPhraseLogitsProcessor(phrase, runner.tokenizer, batch_size)]
))
LLM 響應:妙蛙種子是《寶可夢》系列中的虛構寶可夢。它是一種草系和毒系的寶可夢,其特點是獨特的外觀。感謝您試用我們的 RAG 應用程式!如果您對妙蛙種子有更多疑問,請隨時提出。
每次生成時,我們都能夠在生成結束前新增 `phrase` 字串。
4. MultipleChoiceLogitsProcessor
引導模型透過選擇給定選項之一來回答多項選擇題。
此處理器在需要嚴格遵守結構化答案格式的任務中特別有用,例如測驗、調查或決策支援系統。
example_prompts = [
"""
I am getting a lot of calls during the day. What is more important for me to consider when I buy a new phone?
0. Camera
1. Battery
2. Operating System
3. Screen Resolution
Answer:
""",
]
mclp = MultipleChoiceLogitsProcessor(
runner.tokenizer,
choices=["0", "1", "2", "3"],
delimiter="."
)
print(runner.generate_response(example_prompts, [mclp], max_tokens=1))
LLM 響應:1
在這裡,我們的模型除了選項之外什麼都沒有生成。這在使用代理或將模型用於多項選擇題時是一個非常有用的屬性。
總結
無論您是生成簡潔摘要、編寫聊天機器人響應,還是解決多項選擇題等結構化任務,logit 處理器都提供了有效控制輸出的靈活性。這使得它們在需要精確性、遵守約束或任務特定行為的場景中具有無價的價值。
如果您有興趣進一步探索如何使用 logit 處理器控制生成,以下是一些入門資源:
- 如何使用 Transformers 生成文字 – 🤗 Transformers 中文字生成的入門指南。
- Hugging Face:生成策略 – 瞭解貪婪搜尋、束搜尋和 top-k 取樣等解碼策略。
- Hugging Face:LogitsProcessor API – 深入瞭解 logits 處理在 🤗 Transformers 中如何工作以及如何建立自定義 logits 處理器。
- NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo – 探索 NVIDIA 庫中可用的所有 logits 處理器,包括示例和用例。
藉助 NVIDIA 的 LogitsProcessorZoo 和 Hugging Face 的工具,您擁有一個強大的生態系統,可以將您的語言模型應用程式提升到新的水平。嘗試這些庫,構建自定義解決方案,並與社群分享您的創作,以突破生成式 AI 的可能性邊界。