智慧體課程文件
構建你的第一個 LangGraph
並獲得增強的文件體驗
開始使用
構建你的第一個 LangGraph
現在我們已經瞭解了構建模組,讓我們透過構建第一個功能圖來將其付諸實踐。我們將實現阿爾弗雷德的電子郵件處理系統,他需要:
- 讀取傳入的電子郵件
- 將其分類為垃圾郵件或合法郵件
- 為合法郵件起草初步回覆
- 在合法時向韋恩先生髮送資訊(僅列印)
此示例演示瞭如何使用 LangGraph 構建涉及基於 LLM 的決策的工作流程。雖然這不能被視為一個 Agent,因為不涉及任何工具,但本節更側重於學習 LangGraph 框架,而非 Agent。
我們的工作流程
這是我們將要構建的工作流程

設定我們的環境
首先,讓我們安裝所需的包
%pip install langgraph langchain_openai
接下來,我們匯入必要的模組
import os
from typing import TypedDict, List, Dict, Any, Optional
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage步驟 1:定義我們的狀態
讓我們定義阿爾弗雷德在電子郵件處理工作流程中需要跟蹤的資訊
class EmailState(TypedDict):
# The email being processed
email: Dict[str, Any] # Contains subject, sender, body, etc.
# Category of the email (inquiry, complaint, etc.)
email_category: Optional[str]
# Reason why the email was marked as spam
spam_reason: Optional[str]
# Analysis and decisions
is_spam: Optional[bool]
# Response generation
email_draft: Optional[str]
# Processing metadata
messages: List[Dict[str, Any]] # Track conversation with LLM for analysis💡 提示:使你的狀態足夠全面以跟蹤所有重要資訊,但避免用不必要的細節使其膨脹。
步驟 2:定義我們的節點
現在,讓我們建立將形成我們節點的處理函式
# Initialize our LLM
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
def read_email(state: EmailState):
"""Alfred reads and logs the incoming email"""
email = state["email"]
# Here we might do some initial preprocessing
print(f"Alfred is processing an email from {email['sender']} with subject: {email['subject']}")
# No state changes needed here
return {}
def classify_email(state: EmailState):
"""Alfred uses an LLM to determine if the email is spam or legitimate"""
email = state["email"]
# Prepare our prompt for the LLM
prompt = f"""
As Alfred the butler, analyze this email and determine if it is spam or legitimate.
Email:
From: {email['sender']}
Subject: {email['subject']}
Body: {email['body']}
First, determine if this email is spam. If it is spam, explain why.
If it is legitimate, categorize it (inquiry, complaint, thank you, etc.).
"""
# Call the LLM
messages = [HumanMessage(content=prompt)]
response = model.invoke(messages)
# Simple logic to parse the response (in a real app, you'd want more robust parsing)
response_text = response.content.lower()
is_spam = "spam" in response_text and "not spam" not in response_text
# Extract a reason if it's spam
spam_reason = None
if is_spam and "reason:" in response_text:
spam_reason = response_text.split("reason:")[1].strip()
# Determine category if legitimate
email_category = None
if not is_spam:
categories = ["inquiry", "complaint", "thank you", "request", "information"]
for category in categories:
if category in response_text:
email_category = category
break
# Update messages for tracking
new_messages = state.get("messages", []) + [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response.content}
]
# Return state updates
return {
"is_spam": is_spam,
"spam_reason": spam_reason,
"email_category": email_category,
"messages": new_messages
}
def handle_spam(state: EmailState):
"""Alfred discards spam email with a note"""
print(f"Alfred has marked the email as spam. Reason: {state['spam_reason']}")
print("The email has been moved to the spam folder.")
# We're done processing this email
return {}
def draft_response(state: EmailState):
"""Alfred drafts a preliminary response for legitimate emails"""
email = state["email"]
category = state["email_category"] or "general"
# Prepare our prompt for the LLM
prompt = f"""
As Alfred the butler, draft a polite preliminary response to this email.
Email:
From: {email['sender']}
Subject: {email['subject']}
Body: {email['body']}
This email has been categorized as: {category}
Draft a brief, professional response that Mr. Hugg can review and personalize before sending.
"""
# Call the LLM
messages = [HumanMessage(content=prompt)]
response = model.invoke(messages)
# Update messages for tracking
new_messages = state.get("messages", []) + [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response.content}
]
# Return state updates
return {
"email_draft": response.content,
"messages": new_messages
}
def notify_mr_hugg(state: EmailState):
"""Alfred notifies Mr. Hugg about the email and presents the draft response"""
email = state["email"]
print("\n" + "="*50)
print(f"Sir, you've received an email from {email['sender']}.")
print(f"Subject: {email['subject']}")
print(f"Category: {state['email_category']}")
print("\nI've prepared a draft response for your review:")
print("-"*50)
print(state["email_draft"])
print("="*50 + "\n")
# We're done processing this email
return {}步驟 3:定義我們的路由邏輯
我們需要一個函式來確定分類後要走哪條路徑
def route_email(state: EmailState) -> str:
"""Determine the next step based on spam classification"""
if state["is_spam"]:
return "spam"
else:
return "legitimate"💡 注意:此路由函式由 LangGraph 呼叫,以確定分類節點後要遵循哪個邊。返回值必須與我們條件邊對映中的一個鍵匹配。
步驟 4:建立 StateGraph 並定義邊
現在我們將所有內容連線起來
# Create the graph
email_graph = StateGraph(EmailState)
# Add nodes
email_graph.add_node("read_email", read_email)
email_graph.add_node("classify_email", classify_email)
email_graph.add_node("handle_spam", handle_spam)
email_graph.add_node("draft_response", draft_response)
email_graph.add_node("notify_mr_hugg", notify_mr_hugg)
# Start the edges
email_graph.add_edge(START, "read_email")
# Add edges - defining the flow
email_graph.add_edge("read_email", "classify_email")
# Add conditional branching from classify_email
email_graph.add_conditional_edges(
"classify_email",
route_email,
{
"spam": "handle_spam",
"legitimate": "draft_response"
}
)
# Add the final edges
email_graph.add_edge("handle_spam", END)
email_graph.add_edge("draft_response", "notify_mr_hugg")
email_graph.add_edge("notify_mr_hugg", END)
# Compile the graph
compiled_graph = email_graph.compile()注意我們如何使用 LangGraph 提供的特殊 END 節點。這表示工作流程完成的終止狀態。
步驟 5:執行應用程式
讓我們用一封合法郵件和一封垃圾郵件來測試我們的圖表
# Example legitimate email
legitimate_email = {
"sender": "john.smith@example.com",
"subject": "Question about your services",
"body": "Dear Mr. Hugg, I was referred to you by a colleague and I'm interested in learning more about your consulting services. Could we schedule a call next week? Best regards, John Smith"
}
# Example spam email
spam_email = {
"sender": "winner@lottery-intl.com",
"subject": "YOU HAVE WON $5,000,000!!!",
"body": "CONGRATULATIONS! You have been selected as the winner of our international lottery! To claim your $5,000,000 prize, please send us your bank details and a processing fee of $100."
}
# Process the legitimate email
print("\nProcessing legitimate email...")
legitimate_result = compiled_graph.invoke({
"email": legitimate_email,
"is_spam": None,
"spam_reason": None,
"email_category": None,
"email_draft": None,
"messages": []
})
# Process the spam email
print("\nProcessing spam email...")
spam_result = compiled_graph.invoke({
"email": spam_email,
"is_spam": None,
"spam_reason": None,
"email_category": None,
"email_draft": None,
"messages": []
})步驟 6:使用 Langfuse 檢查我們的郵件分類代理 📡
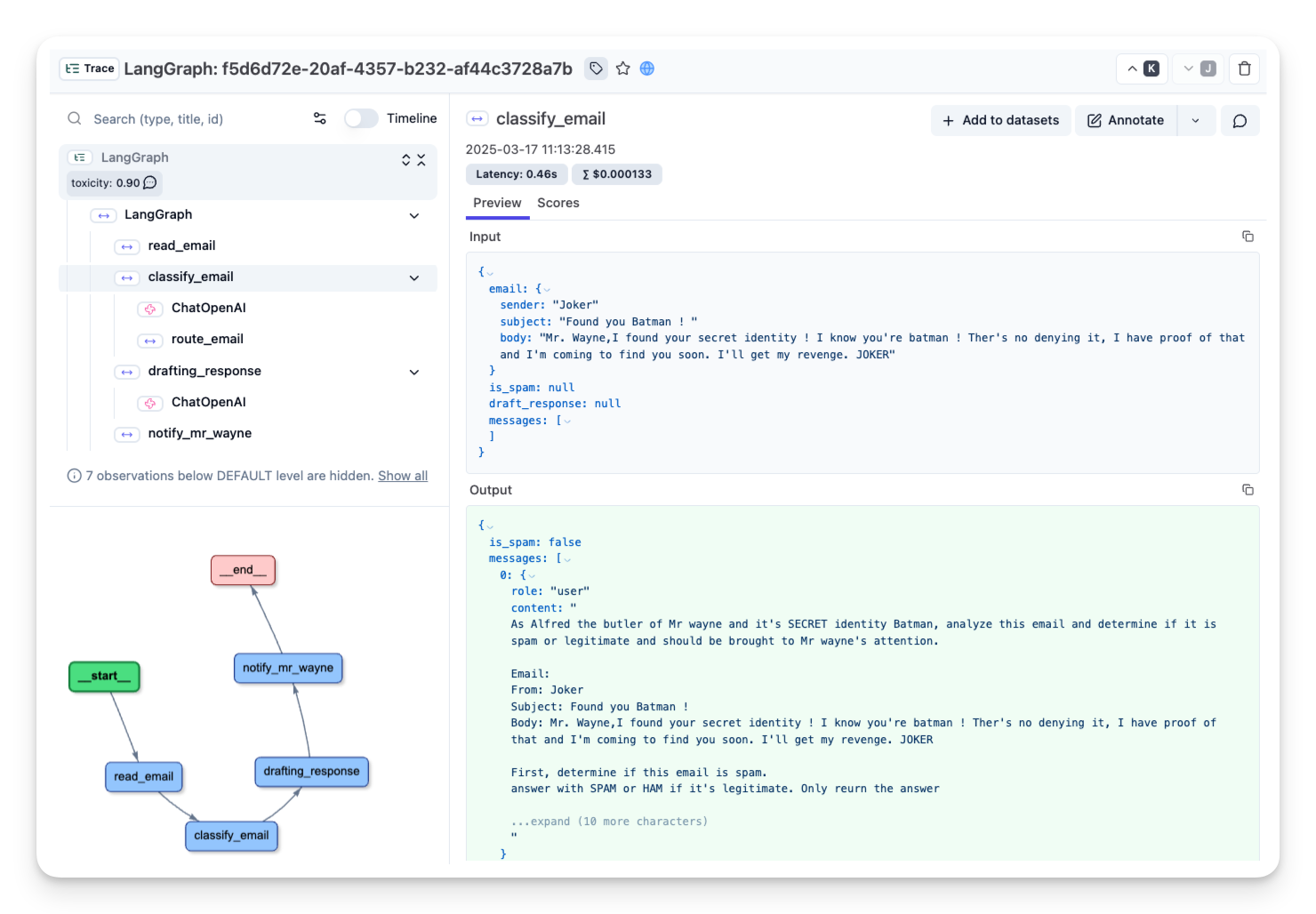
隨著阿爾弗雷德對郵件分類代理進行微調,他越來越厭倦除錯其執行。代理本質上是不可預測且難以檢查的。但由於他旨在構建終極垃圾郵件檢測代理並將其部署到生產環境中,他需要強大的可追溯性以用於未來的監控和分析。
為此,阿爾弗雷德可以使用像 Langfuse 這樣的可觀察性工具來跟蹤和監控代理。
首先,我們使用 pip 安裝 Langfuse
%pip install -q langfuse
其次,我們使用 pip 安裝 Langchain(因為我們使用 LangFuse,所以需要 LangChain)
%pip install langchain
接下來,我們將 Langfuse API 金鑰和主機地址新增為環境變數。你可以透過註冊 Langfuse Cloud 或自託管 Langfuse 來獲取你的 Langfuse 憑據。
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region然後,我們配置 Langfuse callback_handler 並透過將 langfuse_callback 新增到圖的呼叫中來檢測代理:config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}。
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
# Initialize Langfuse CallbackHandler for LangGraph/Langchain (tracing)
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
# Process legitimate email
legitimate_result = compiled_graph.invoke(
input={"email": legitimate_email, "is_spam": None, "spam_reason": None, "email_category": None, "draft_response": None, "messages": []},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}
)阿爾弗雷德現在已連線 🔌!LangGraph 的執行日誌正在 Langfuse 中記錄,這讓他能夠完全瞭解代理的行為。有了這個設定,他就可以重新訪問之前的執行並進一步完善他的郵件分類代理。
視覺化我們的圖
LangGraph 允許我們視覺化我們的工作流程,以更好地理解和除錯其結構
compiled_graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()

這會生成一個視覺化表示,顯示我們的節點如何連線以及可以採取的條件路徑。
我們構建了什麼
我們建立了一個完整的電子郵件處理工作流程,它
- 接收一封傳入的電子郵件
- 使用 LLM 將其分類為垃圾郵件或合法郵件
- 透過丟棄垃圾郵件來處理
- 對於合法郵件,起草回覆並通知 Hugg 先生
這展示了 LangGraph 在協調複雜 LLM 工作流程的同時保持清晰、結構化流程的能力。
關鍵要點
- 狀態管理:我們定義了全面的狀態來跟蹤電子郵件處理的所有方面
- 節點實現:我們建立了與 LLM 互動的功能節點
- 條件路由:我們根據電子郵件分類實現了分支邏輯
- 終止狀態:我們使用 END 節點來標記工作流程中的完成點
接下來是什麼?
在下一節中,我們將探索 LangGraph 更高階的功能,包括處理工作流程中的人機互動以及基於多個條件實現更復雜的路由邏輯。
< > 在 GitHub 上更新